As a member of the military in Germany, you can benefit from special regulations that facilitate access to hunting and the acquisition of firearms. These exceptions are based on the Weapons Act (§ 55 WaffG) and apply to both German and foreign military personnel under certain conditions. Here are the key points:
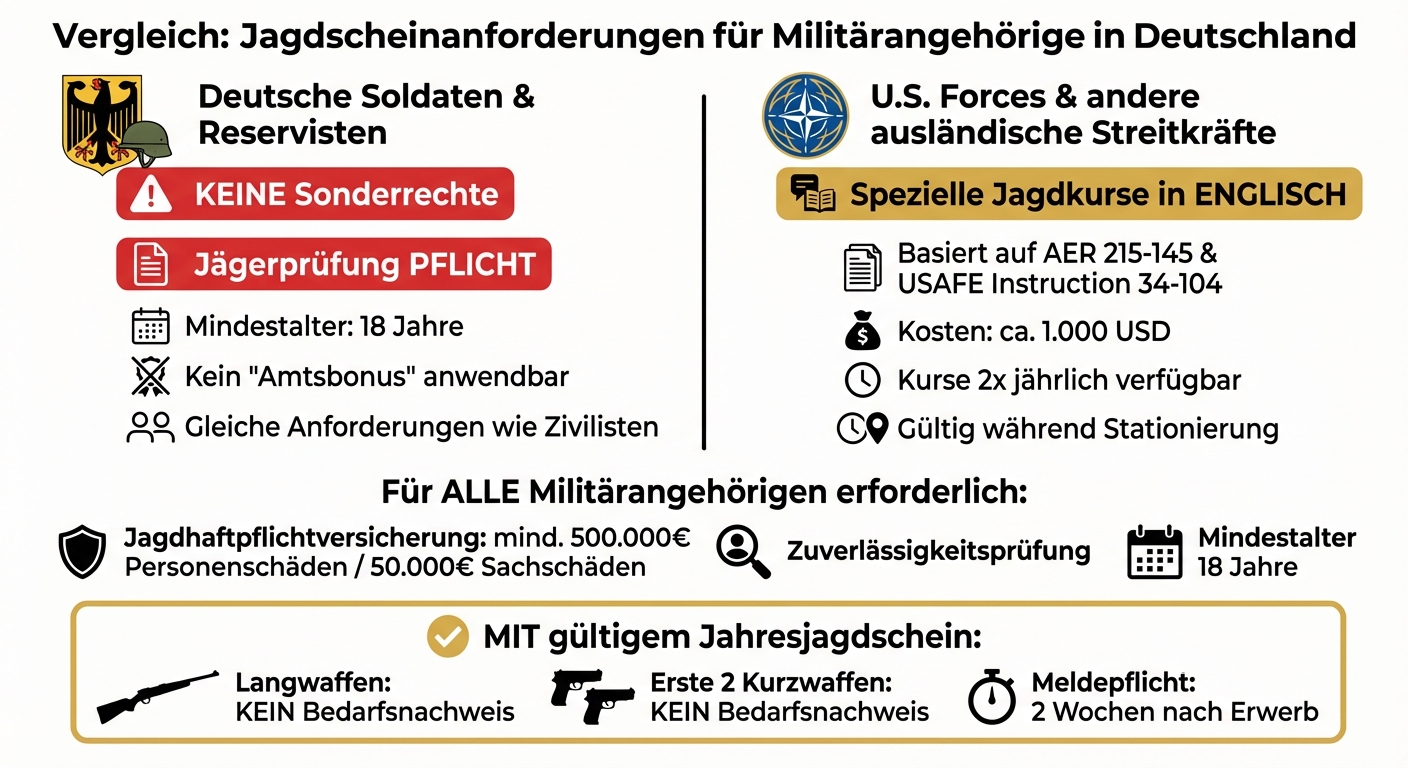
- German military personnel must pass the hunter's exam like everyone else to obtain a hunting license. There are no special rights for private firearm acquisition.
- Foreign military personnel, such as members of the U.S. Forces, can complete special hunting courses in English that are recognized by the German government.
- With a valid annual hunting license, the proof of need for long guns and the first two handguns is waived.
- The application is made at the responsible hunting authority, requiring documents such as an ID card, hunter's exam certificate, and hunting liability insurance.
Important: The regulations vary regionally and apply only for the duration of the posting in Germany. There are strict requirements for firearm acquisition and transport that must be adhered to.
Hunting License Requirements for German and Foreign Military Personnel in Germany
Basics of the Hunting License for Military Personnel
To better understand the special reliefs for military personnel, it is worthwhile to first look at the general requirements for the hunting license in Germany.
What is a Hunting License?
A hunting license is your official permission to hunt in Germany. According to § 15 of the Federal Hunting Act (BJagdG), you may only participate actively in hunting with a valid hunting license [5]. This license is valid nationwide, regardless of which federal state it was issued in.
To obtain a regular hunting license, you must be at least 18 years old, successfully pass the German hunter's exam, and demonstrate your reliability and personal suitability. Additionally, hunting liability insurance is required, covering at least €500,000 for personal injury and €50,000 for property damage [3]. With a valid annual hunting license, you can acquire long guns, while for handguns, an entry in the firearm ownership card is necessary beforehand.
These requirements also apply to military personnel, although special exceptions exist for them. These basic requirements form the legal framework upon which the military special regulations are built.
Legal Framework for Military Exceptions
Although the general requirements apply to everyone, military personnel benefit from special exceptions. These are based on the Federal Hunting Act (BJagdG) and the Weapons Act (WaffG) [1]. While § 15 BJagdG regulates the hunting license requirement for all, § 55 WaffG provides extensive exemptions – particularly for the Bundeswehr, federal and state authorities, and the police, especially in official contexts [4].
Foreign hunting licenses, on the other hand, do not entitle holders to hunt or acquire firearms in Germany. Therefore, special regulations apply to foreign military personnel [3]. The responsible authorities regularly check your reliability, including inquiries with the Office for the Protection of the Constitution and other registers [3]. Your military training can be recognized as proof of the required expertise, which provides you with certain administrative reliefs.
sbb-itb-1cfd233
Exceptions for Foreign Military Personnel
This section highlights special regulations for foreign military personnel stationed in Germany. If you belong to this group, bilateral agreements may facilitate your access to hunting – and that without the regular German-language hunter's exam.
Regulations for Foreign Military Personnel
The German government allows the U.S. Forces in Europe to offer independent hunting courses in English. These are based on the Army Europe Regulation (AER) 215-145 and the U.S. Air Forces Europe Instruction 34-104 [8]. Instead of the state German exam, you complete a course recognized by the U.S. Forces.
These courses take place at certain U.S. military bases and cover topics such as flora and fauna, firearm handling, and shooting techniques [7][8]. The exam consists of written tests and a practical shooting test, where targets such as “Running Boar,” “Running Rabbit,” and clay pigeons are shot [7][8].
“The German government allows the U.S. Forces in Europe to conduct courses that enable U.S. Forces personnel to qualify for a foreign hunting license." – U.S. Army MWR [8]
The cost for this course is about $1,000, which is significantly cheaper compared to the usual fees for German civilians [8]. In the next section, you will learn what documents you need.
Required Documents
To apply for your foreign hunting license, you must submit the following documents:
- The AE Form 215-145A (Application for Issuance/Renewal of a German Hunting License) [8]
- Your valid U.S. Forces ID as proof of your posting [8]
- The completion certificate of the U.S. Forces hunting course as proof of your hunting knowledge [7]
- Proof of your statutory hunting liability insurance and two passport photos for the initial application [6][8]
- The AE Form 190-6Ha/Hb (Commander's Statement of Reliability) for the reliability check according to German firearms law [8]
Since the courses are only offered twice a year and you must be at least 18 years old, it is advisable to contact your local Outdoor Recreation (ODR) office early [8].
Exceptions for German Military Personnel and Reservists
German soldiers and reservists do not enjoy special status when it comes to acquiring a hunting license. They must meet the same requirements as everyone else. Here are the exact prerequisites and changes resulting from recent reforms summarized.
Requirements for German Military Personnel
For German soldiers, there is no so-called official bonus that facilitates access to private hunting. Unlike police officers, who can prove their personal suitability according to § 6 WaffG with a certificate from their superior, this option is explicitly excluded for soldiers [9].
“The so-called 'official bonus' does not apply to soldiers." – General Administrative Regulation on the Weapons Act (WaffVwV) [10]
Military training is solely geared towards official deployment. For private use, soldiers must demonstrate safe handling of firearms by successfully completing the hunter's exam – often referred to as the “Green Abitur.” This means they must be at least 18 years old like any other applicant, prove their reliability, and pass the exams [11][12].
The regulations from § 55 WaffG apply only to official use. For private activities, the hunter's exam remains mandatory. This clear separation was recently confirmed by an amendment to the Weapons Act on July 17, 2025 (BGBl. 2025 I No. 171) [12].
Effects of Current Service Time Reforms
The Military Service Modernization Act, which comes into effect in 2026, strengthens the reserves but has no impact on the hunting license requirements. The federal government plans to increase the number of reservists to 200,000 by 2035, in addition to more than 260,000 active soldiers [13]. Starting in 2026, a digital suitability questionnaire will be introduced for all 18-year-olds, and from July 1, 2027, medical examinations will be mandatory for men born in 2008 [14][15].
Despite these reforms, the requirements for the hunting license remain unchanged. Even though the systematic recording of fitness and reliability could theoretically facilitate administrative processes, the hunter's exam remains mandatory for all German soldiers and reservists [16].
If you have passed the hunter's exam, you can find a wide selection of hunting firearms, optics, and accessories at Gunfinder – everything you need for your equipment.
Application Process and Responsible Authorities
Step-by-Step Guide to Application
The general requirements of the regional hunting authorities also apply to military personnel. You apply for your hunting license at the responsible district or regulatory office [1][3]. If you are unsure which authority is responsible for you, you can contact the central service number 115. This is available Monday to Friday from 08:00 to 18:00 [1][3]. To ensure a smooth application process, you will need some important documents.
The required documents include: the completed application form for your region, a valid ID card or passport, your hunter's exam certificate, one to two recent passport photos, and proof of hunting liability insurance [1][3]. As explained in the section “What is a Hunting License?”, the insurance must cover at least €500,000 for personal injury and €50,000 for property damage and be valid for the entire duration of the hunting license [3].
Once you have all the documents ready, you can submit the application. Many federal states, including Baden-Württemberg, now offer online portals like Service-BW through which you can submit your application digitally. However, for the initial application, personal appearance is usually required [3]. Before issuing the hunting license, the authority conducts a reliability check, during which your suitability according to firearms and hunting law is verified [1][3]. This check is usually repeated every three years [3].
The fees for the hunting license vary. In Stuttgart, for example, a one-year license costs €117, while a three-year license costs €284 [3]. In Thuringia, the costs are €70 for one year and €135 for three years [1]. Additionally, there is the option to apply for a one-day hunting license for 14 days, which costs €45 in Thuringia [1]. The fees consist of an administrative fee and the hunting fee [3].
Regional Differences
Although the required documents are uniform nationwide, there are regional differences in submission methods and processing times. For example, Baden-Württemberg offers an integrated service account that allows you to track the status of your application online. Other federal states still rely on paper forms that must be submitted by mail or in person [1][3]. The processing time largely depends on how quickly the involved authorities – such as the police or the Office for the Protection of the Constitution – complete the reliability check [1][5].
The fees are also not uniformly regulated, as each municipality or district sets the amount itself [1][3]. While a three-year license costs €135 in Thuringia, more than double is charged in Stuttgart [1][3]. Make sure to always use the form from your responsible authority to avoid delays [3].
Restrictions and Conditions for Military Hunting Licenses
Restrictions on Firearm Acquisition
Once you have successfully completed the application process for the hunting license, certain restrictions apply in firearms and hunting law: With a German annual hunting license, you can purchase long guns and associated ammunition without additional acquisition permission [2]. However, for handguns such as pistols or revolvers, an entry in your firearm ownership card (WBK) is required before you may possess them [2].
As a military member with a German hunting license, you benefit from the so-called “hunter's quota”: For long guns and the first two handguns, you do not need to provide additional proof of need – this is automatically recognized [2]. Important: Every newly acquired firearm must be reported to the responsible authority within two weeks [2].
When transporting firearms, they must be unloaded and stored in such a way that they are not readily accessible. Loading is only permitted at the edge of the hunting area [2]. For holders of a youth hunting license, permanent acquisition of their own firearms remains excluded [2].
Territorial and Temporal Restrictions
In addition to the firearms law requirements, there are also clear spatial and temporal restrictions on the use of the hunting license. Foreign military personnel are subject to stricter rules: Their hunting licenses are often only valid for the duration of their service in Germany and are limited to specific areas – for example, federal or state forests with explicit hunting permission [17]. In Bavaria, the hunting license for foreign military personnel is usually issued by the hunting authority at their respective place of service [17].
Violations of these regulations are costly: Hunting without a valid license can cost between €500 and €1,500, while hunting in unauthorized areas is penalized with fines of €100 to €1,000 [18].
Conclusion: Hunting License Exceptions for Military Personnel – Summary
The fundamental requirements for the hunting license remain unchanged: You must be at least 18 years old, have passed the hunter's exam, be able to prove your reliability, and obtain hunting liability insurance with a coverage amount of at least €500,000 for personal injury [2]. Here are the key special regulations and practical tips summarized.
A major advantage for hunters in Germany is the so-called “hunter's quota.” With a valid German annual hunting license, the additional proof of need for long guns and the first two handguns is waived. This need is automatically recognized by law [2].
Foreign military personnel, such as members of the U.S. Forces in Germany, are often subject to special regulations tied to their service time. It is recommended to inform yourself about the “U.S. Forces Europe Hunting, Fishing, and Sport Shooting Program” to learn all the details [2].
When you acquire a new firearm, you must report it to the responsible authority within two weeks [2]. Also, pay attention to the requirements for safe storage and transport: Firearms must be stored in certified safes (VDMA 24992 Class A or B). During transport, they must neither be loaded nor readily accessible [2].
To apply for the hunting license, contact the lower hunting authority at your place of residence or service. Bring all required documents, including proof of passing the hunter's exam, your valid ID card, and the insurance confirmation. As already described, these regulations provide a clear framework for firearm acquisition and safe storage – essential foundations for all hunters. If you have questions about regional specifics, your responsible hunting authority will assist you.
FAQs
What special rules apply to former military personnel?
Former military personnel have the opportunity to obtain a hunting permit under certain conditions. It is particularly important that they meet personal suitability criteria such as mental and physical health as well as reliability. These requirements differ little from those that apply to other applicants.
Does the foreign hunting license remain valid after a transfer out of Germany?
The foreign hunting license is generally only valid for the duration of the granted permit. If the person is transferred out of Germany, the hunting license usually automatically loses its validity and must be reapplied for.
Which firearms can I purchase immediately with a hunting license?
In Germany, a valid hunting license allows you to immediately purchase hunting firearms, such as shotguns, rifles, and handguns that are specifically approved for hunting. It is important that these firearms are neither prohibited nor violate legal regulations.